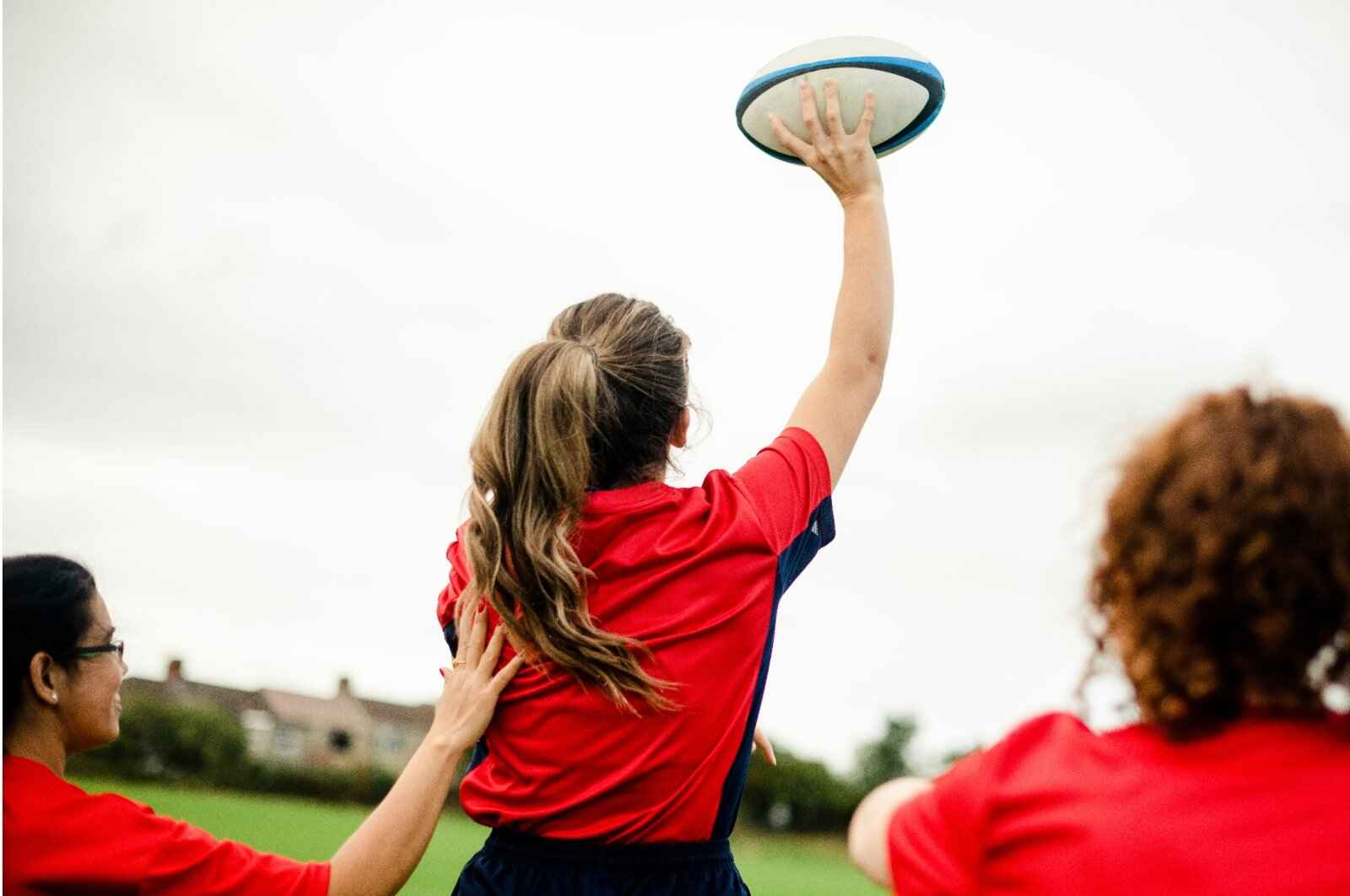
Introduction
Throwing A Rugby Ball: it is a fundamental skill that every rugby player must master. Unlike the more straightforward throwing techniques in other sports, rugby passes require precision, control, and an understanding of the unique shape and weight of the ball. This blog post delves into the essential techniques for throwing a rugby ball, the mechanics behind effective passing, and the drills that can help players refine their skills.
Understanding The Basics Of Rugby Passing
Throwing A Rugby Ball, The rugby ball is distinct in its oval shape, which influences how it should be handled and thrown. Mastering the basics of passing involves understanding grip, body positioning, and the mechanics of the throw itself. These elements combine to produce a pass that is accurate, controlled, and appropriate for the game situation.
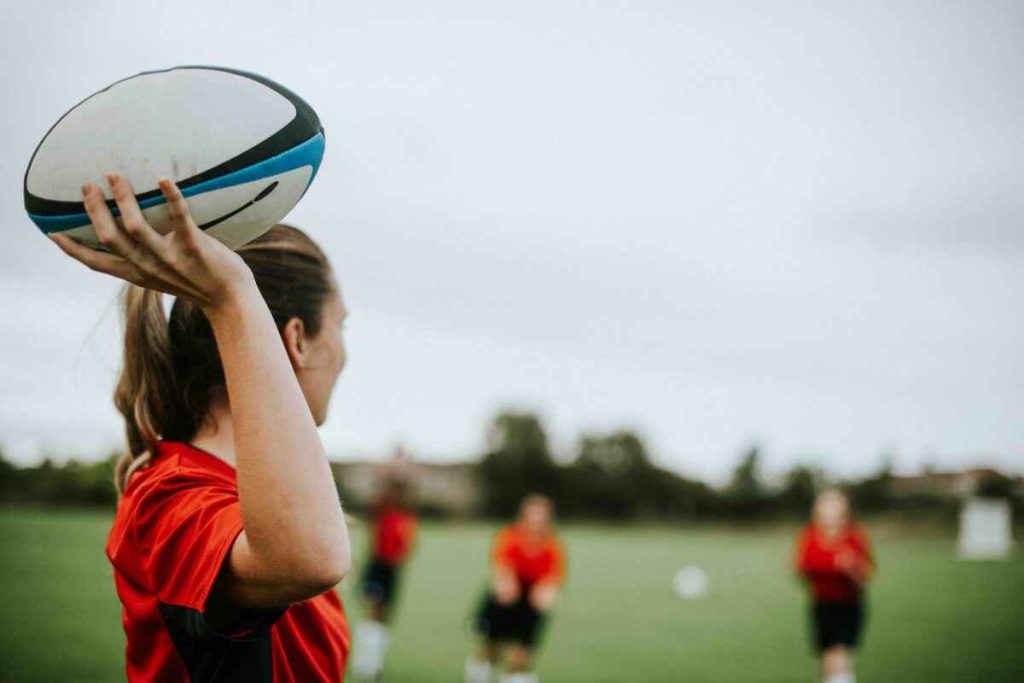

Grip And Hand Position
Throwing A Rugby Ball, The grip on the rugby ball is crucial for control and accuracy. Unlike throwing a round ball, where the grip can be more flexible, a rugby ball requires a specific hand placement. The hands should be spread along the seams of the ball, with the thumbs placed underneath and the fingers wrapping around the top. This grip allows for better control and the ability to generate spin on the ball, which is essential for a stable and accurate pass. The dominant hand typically provides the power, while the non-dominant hand guides the direction.
Body Positioning And Stance
Proper body positioning and stance are vital for an effective rugby pass. The feet should be shoulder-width apart, with the body slightly angled towards the target. This stance provides a stable base and allows for a fluid transfer of weight during the throw. The knees should be slightly bent to maintain balance and enable quick movement. The shoulders and hips should align with the target, ensuring that the entire body works together to direct the ball accurately.
Throwing A Rugby Ball: Mechanics Of The Throw
The mechanics of the rugby pass involve a coordinated movement of the arms, wrists, and body. The throw starts with the ball held at chest height. As the pass begins, the hands guide the ball, while the dominant hand imparts spin by flicking the wrist. The body rotates slightly to add power and direction to the pass. The follow-through is crucial; the arms should extend fully towards the target, and the body should move fluidly in the direction of the throw. This coordinated movement ensures that the ball travels accurately and with the desired spin.
Different Types Of Rugby Passes
Throwing A Rugby Ball, Rugby involves various types of passes, each suited to specific game situations. Understanding and mastering these different passes can greatly enhance a player’s versatility and effectiveness on the field. Key passes include the spin pass, the pop pass, and the switch pass, among others.
Spin Pass
Throwing A Rugby Ball, The spin pass, or spiral pass, is one of the most common and effective passes in rugby. It involves spinning the ball to maintain its stability and accuracy over longer distances. The technique requires a firm grip on the ball, a flick of the wrists, and a coordinated follow-through. The spin pass is particularly useful for transferring the ball quickly across the field, allowing teammates to catch it cleanly and maintain the flow of the game.
Pop Pass
Throwing A Rugby Ball, The pop pass is a shorter, quicker pass used in close quarters. It involves a gentle flick of the wrists to lift the ball slightly into the air, allowing a teammate to catch it easily. The pop pass is effective for offloading the ball during contact situations or when the passer is about to be tackled. The key to a successful pop pass is maintaining control and ensuring that the ball is delivered accurately to the teammate.
Switch Pass
The switch pass, or dummy pass, is a deceptive move designed to confuse defenders. It involves faking a pass in one direction before quickly switching and delivering the ball in another direction. The switch pass requires quick hand movements and a good understanding of timing and positioning. It can create space and opportunities by wrong-footing defenders and opening up gaps in the defensive line.
Drills To Improve Passing Skills
Throwing A Rugby Ball, Practicing various drills is essential for developing and refining rugby passing skills. These drills focus on different aspects of the pass, such as accuracy, speed, and coordination, helping players become more proficient and confident in their passing abilities.
Stationary Passing Drills
Stationary passing drills involve practicing passes without moving, focusing on technique and accuracy. Players can work in pairs, standing a few meters apart, and pass the ball back and forth. This drill emphasizes proper grip, hand positioning, and follow-through. It allows players to concentrate on the mechanics of the pass and develop muscle memory.
Throwing A Rugby Ball: Moving Passing Drills
Moving passing drills incorporate movement and game-like scenarios to enhance passing skills. Players can run in parallel lines, passing the ball while on the move. This drill simulates real-game situations, helping players learn to pass accurately under pressure and while running. It also improves coordination and timing, as players must adjust their passes based on the movement of their teammates.
Target Passing Drills
Throwing A Rugby Ball, Target passing drills involve passing the ball to specific targets, such as cones or markers, placed at varying distances and angles. This drill enhances accuracy and precision, requiring players to focus on hitting the target consistently. It can be made more challenging by incorporating movement or adding defenders to simulate game conditions.
Common Mistakes And How To Avoid Them

Even experienced players can make mistakes when throwing a rugby ball. Identifying and correcting these mistakes is crucial for improving passing skills and ensuring effective gameplay.
Overreliance On Arms
One common mistake is relying too much on the arms to generate power, neglecting the role of the body in the pass. This can lead to inaccurate and weak passes. To avoid this, players should focus on using their entire body, particularly the rotation of the hips and shoulders, to generate power and direction. Proper body mechanics are essential for a strong and accurate pass.
Throwing A Rugby Ball: Poor Grip And Hand Positioning
Another common mistake is poor grip and hand positioning, which can affect control and accuracy. Players should ensure that their hands are correctly positioned along the seams of the ball, with the thumbs underneath and fingers wrapping around the top. A firm but flexible grip is necessary to control the ball and impart the desired spin.
Inconsistent Follow-Through
Inconsistent follow-through can lead to erratic passes. Players should ensure that their follow-through is smooth and directed towards the target. The arms should extend fully, and the body should move in the direction of the pass. Practicing proper follow-through helps develop consistency and accuracy in passing.
The Role Of Passing In Game Strategy
Passing is not just a fundamental skill but also a critical component of game strategy in rugby. Effective passing can create scoring opportunities, maintain possession, and disrupt the opponent’s defense. Understanding the strategic importance of passing enhances a player’s ability to contribute to the team’s success.
Creating Space And Opportunities
Throwing A Rugby Ball, Effective passing can create space and opportunities for attacking plays. By moving the ball quickly and accurately across the field, players can stretch the opponent’s defense and create gaps. Well-timed passes can enable wingers and centers to exploit these gaps, leading to line breaks and scoring opportunities. The ability to pass effectively under pressure is crucial for maintaining the flow of the game and executing strategic plays.
Maintaining Possession
Maintaining possession is vital in rugby, and passing plays a key role in this aspect. Accurate and controlled passes ensure that the team retains possession and can continue their attacking momentum. Poor passes or handling errors can lead to turnovers and give the opponent an advantage. Practicing passing drills and developing strong passing skills help minimize errors and maintain possession.
Disrupting Opponent’s Defense
Throwing A Rugby Ball, Passing can also be used strategically to disrupt the opponent’s defense. Quick and unexpected passes can catch defenders off guard and create confusion. The switch pass, for example, can wrong-foot defenders and open up attacking opportunities. Effective communication and coordination among players are essential for executing passes that disrupt the opponent’s defensive structure.
Advanced Passing Techniques
As players become more proficient in basic passing skills, they can explore advanced techniques to enhance their gameplay. These techniques require a higher level of skill and understanding of the game but can significantly impact a team’s performance.
Off-Load Passing
Throwing A Rugby Ball, Off-load passing is an advanced technique used to keep the ball alive during contact situations. It involves passing the ball to a teammate while being tackled or just before being tackled. This requires quick decision-making, spatial awareness, and precise passing skills. Off-load passing can maintain the momentum of the attack and prevent the defense from resetting.
Long Passes
Long passes are used to quickly switch the point of attack and exploit space on the field. These passes require significant power and accuracy, often involving a more pronounced wrist flick and body rotation. Practicing long passes helps players develop the ability to accurately deliver the ball over longer distances, creating opportunities for wide attacks.
Dummy Passes
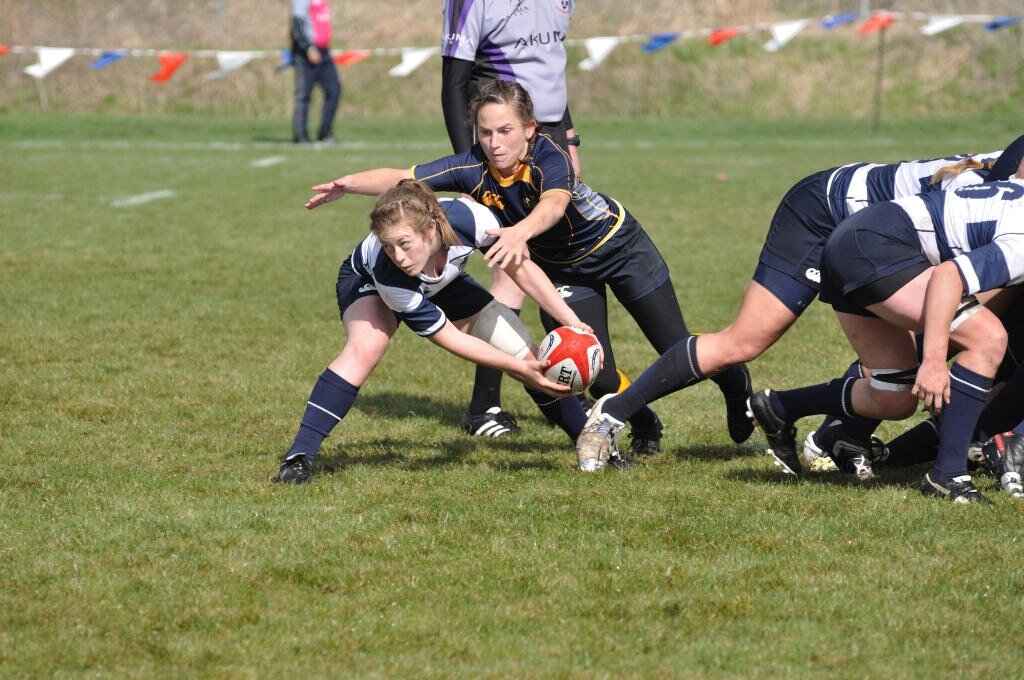

Dummy passes are deceptive moves designed to confuse defenders. They involve faking a pass to one direction while retaining the ball and passing in another direction. Dummy passes require quick hand movements and a good understanding of timing and positioning. They can create space and opportunities by wrong-footing defenders and opening up gaps in the defensive line.
Conclusion
Throwing A Rugby Ball, Learning how to throw a rugby ball involves mastering various techniques, understanding the mechanics of different passes, and practicing consistently to develop proficiency. Proper grip, body positioning, and follow-through are essential elements of a successful pass. Different types of passes, such as the spin pass, pop pass, and switch pass, serve specific purposes and enhance a player’s versatility on the field. Drills that focus on accuracy, speed, and coordination help refine passing skills and build confidence. Avoiding common mistakes, such as overreliance on arms or poor hand positioning, is crucial for effective passing.
Passing is also a critical component of game strategy, enabling teams to create space, maintain possession, and disrupt the opponent’s defense. Advanced passing techniques, such as off-load passes, long passes, and dummy passes, require higher skill levels but can significantly impact a team’s performance. By understanding the strategic importance of passing and practicing regularly, players can enhance their contribution to the