Introduction
The Cricket World Cup is one of the most prestigious tournaments in international cricket, bringing together the best teams from around the world to compete for the coveted trophy. Organized by the International Cricket Council (ICC), this tournament has evolved over the years, with changing formats and an increasing number of participating teams. The question of how many countries play in the Cricket World Cup depends on the tournament format and the qualification process, which determines the teams that make it to the final event. Understanding the history, format, and qualification process of the Cricket World Cup provides insight into the global reach of the sport and the nations that actively compete at the highest level. Please visit this.
The Origins And Growth Of The Cricket World Cup
The Cricket World Cup was first held in 1975 in England and featured eight teams. The tournament was played in a 60-over format, with matches conducted in traditional white clothing and using red balls. Over the decades, the Cricket World Cup has expanded significantly, with new teams joining and formats evolving to accommodate a larger number of participants. The introduction of colored clothing, white balls, and day-night matches modernized the competition, making it more appealing to a global audience. The growth of the tournament has led to increased participation, with more countries aspiring to qualify and compete on the world stage.
Current Format And Number Of Teams In The Cricket World Cup
The number of teams playing in the Cricket World Cup has varied across different editions of the tournament. In the early years, only a handful of teams participated, but as cricket gained popularity worldwide, the ICC expanded the competition. The most recent editions of the Cricket World Cup have featured 10 teams, following a round-robin format where every team plays against each other before advancing to the knockout stage. However, past tournaments have included up to 16 teams, allowing more associate nations to participate. The ICC continues to evaluate the format, with discussions about further expanding the tournament to accommodate more teams in the future.
Qualification Process For The Cricket World Cup
Not every cricket-playing nation automatically qualifies for the Cricket World Cup. The qualification process is structured to ensure that the best teams make it to the tournament while also providing opportunities for emerging teams to compete. Full member nations of the ICC, such as India, Australia, England, and South Africa, typically have direct qualification pathways based on their rankings. Meanwhile, associate member nations must go through qualifying tournaments such as the ICC Cricket World Cup Qualifier, where teams compete for the remaining spots in the main tournament. This qualification process allows teams from non-traditional cricketing regions to challenge established teams and potentially secure a place in the World Cup.
Full Member Countries That Play In The Cricket World Cup
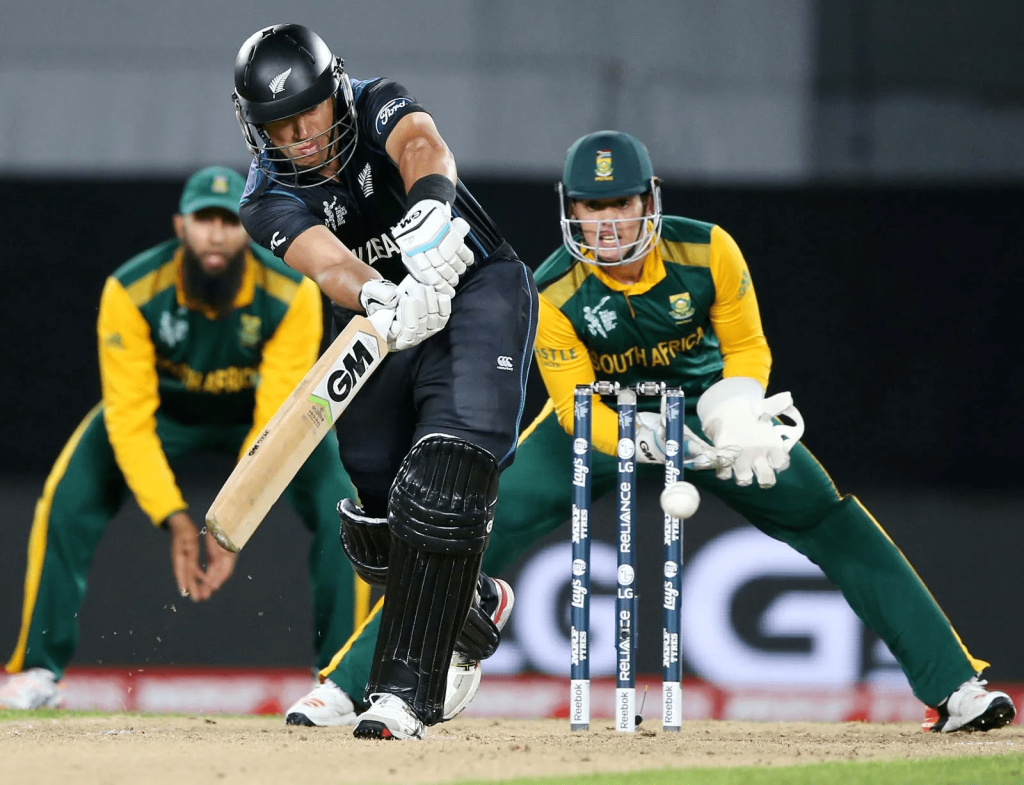

The ICC recognizes 12 full member nations, all of which have played in at least one Cricket World Cup. These full members include India, Australia, England, Pakistan, South Africa, New Zealand, West Indies, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Zimbabwe, Afghanistan, and Ireland. These teams have full Test status and automatically participate in ICC tournaments, including the World Cup, based on their performance in international competitions. While some full member nations have been dominant in World Cup history, others have struggled to qualify in certain editions due to the competitive nature of the qualification process.
Associate Member Nations And Their Participation
In addition to full member nations, several associate member countries have participated in the Cricket World Cup. These teams do not have Test status but have shown significant progress in limited-overs cricket. Countries such as the Netherlands, Scotland, Kenya, Canada, the United Arab Emirates, and Namibia have qualified for the World Cup through the qualification tournaments. Some associate nations have even caused upsets in World Cup history, defeating established teams and making deep runs in the tournament. Their participation highlights the growing reach of cricket and the efforts of the ICC to globalize the sport.
Historic Participation And Changes In Team Numbers
The number of teams in the Cricket World Cup has fluctuated over the years. The first three editions of the tournament (1975, 1979, and 1983) featured eight teams. In 1987, the number of teams was increased to nine, followed by further expansions in the 1992 and 1996 tournaments, which included 12 and 14 teams, respectively. The largest World Cups took place in 2007 and 2011, with 16 and 14 teams participating. However, the ICC later decided to reduce the number of teams to 10 for the 2019 and 2023 editions, focusing on a more competitive structure. The future editions of the tournament may see another expansion as the ICC aims to include more teams from emerging cricketing nations.
Countries That Have Won The Cricket World Cup

While many countries participate in the Cricket World Cup, only a select few have managed to lift the trophy. Australia has been the most dominant team in World Cup history, winning multiple titles. India, England, and West Indies have also claimed the championship on multiple occasions. Sri Lanka and Pakistan have each won the tournament once, showcasing their strength in the cricketing world. The victories of these nations highlight the competitive nature of the tournament and the high level of skill required to win the title.
The Global Reach Of Cricket And The Future Of The World Cup
Cricket continues to grow beyond its traditional strongholds, with emerging nations investing in the sport to compete at higher levels. The inclusion of teams from different continents has broadened the audience for the Cricket World Cup, making it a truly global event. The ICC has been working on expanding the game by promoting cricket in regions like North America, Europe, and East Asia. Future World Cups may see more countries participating, further strengthening cricket’s presence worldwide. With T20 cricket gaining popularity, the shorter format may also play a role in increasing the number of teams in future editions.
Conclusion
The number of countries that play in the Cricket World Cup varies based on the tournament format and qualification process. Historically, the World Cup has featured anywhere between 8 and 16 teams, with the most recent editions hosting 10 teams. Full member nations of the ICC usually dominate the tournament, while associate member nations have opportunities to qualify through structured pathways. As cricket continues to expand, the World Cup may see further increases in the number of participating countries. With its rich history and growing global appeal, the Cricket World Cup remains one of the most prestigious events in the sport, attracting teams from different parts of the world and showcasing the best of international cricket.